Analyzing data from head-mounted eye trackers is complex, from mapping gaze onto dynamic scenes to synchronizing multiple data streams. Blickshift Analytics brings together all the tools needed to handle these challenges in a single, powerful software environment. Our software simplifies the entire process of analyzing data from head-mounted eye trackers, from synchronization and visualization to event-based analysis and quality control. It combines precision, flexibility, and user-friendly design in one tool, empowering researchers to focus on insights rather than data wrangling.
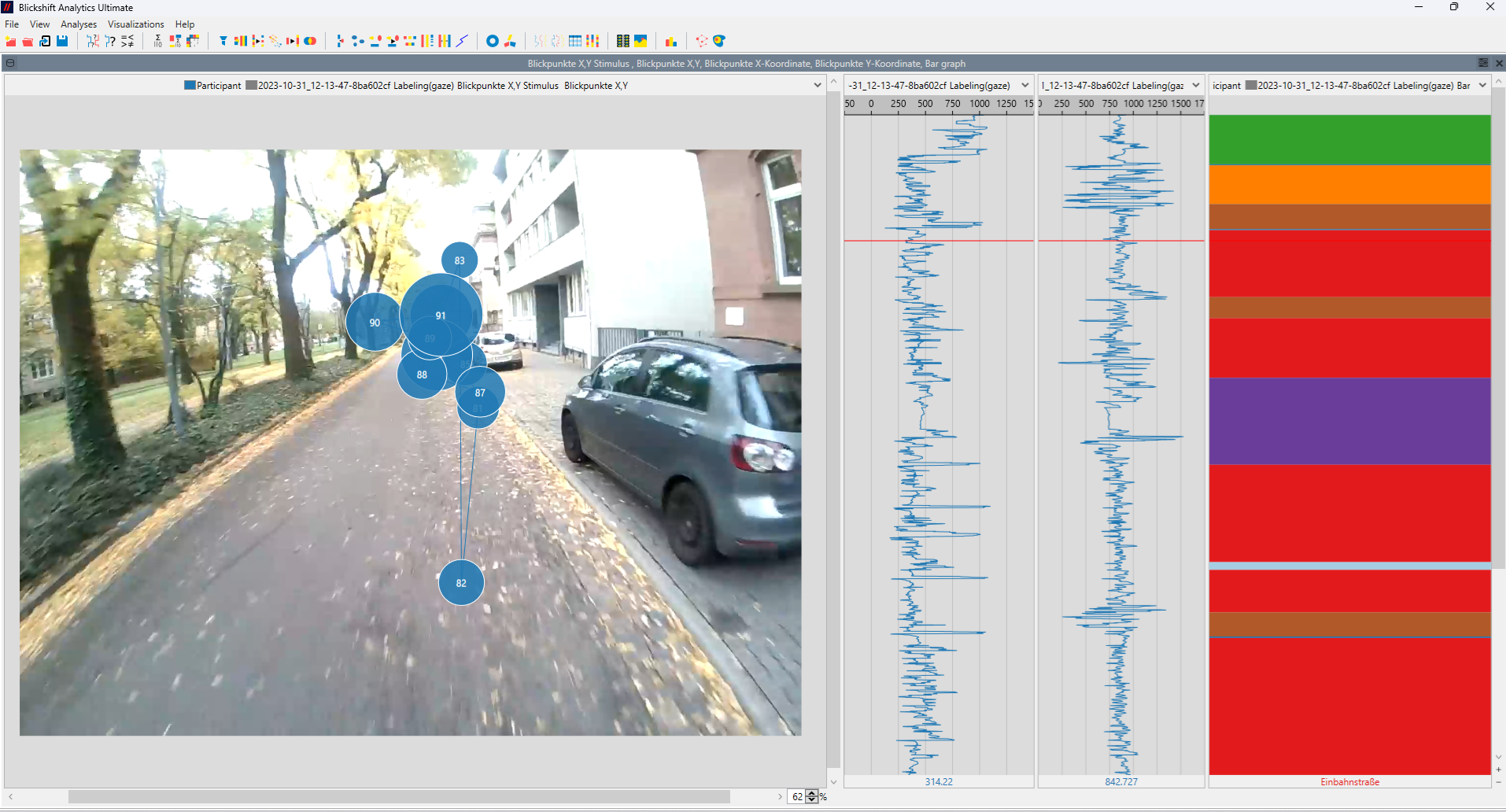
Accurate Mapping of Gaze to the Scene
Challenge: Head-mounted eye trackers record gaze relative to the head or eye camera, not directly in world coordinates. Mapping gaze to real-world objects or areas of interest is difficult.
- Blickshift Analytics integrates scene video visualization with synchronized gaze overlays. The software allows frame-by-frame inspection, automatic correction, and flexible data export. Researchers can combine scene video and gaze data interactively, making it easy to visualize where participants were truly looking — even in dynamic environments.
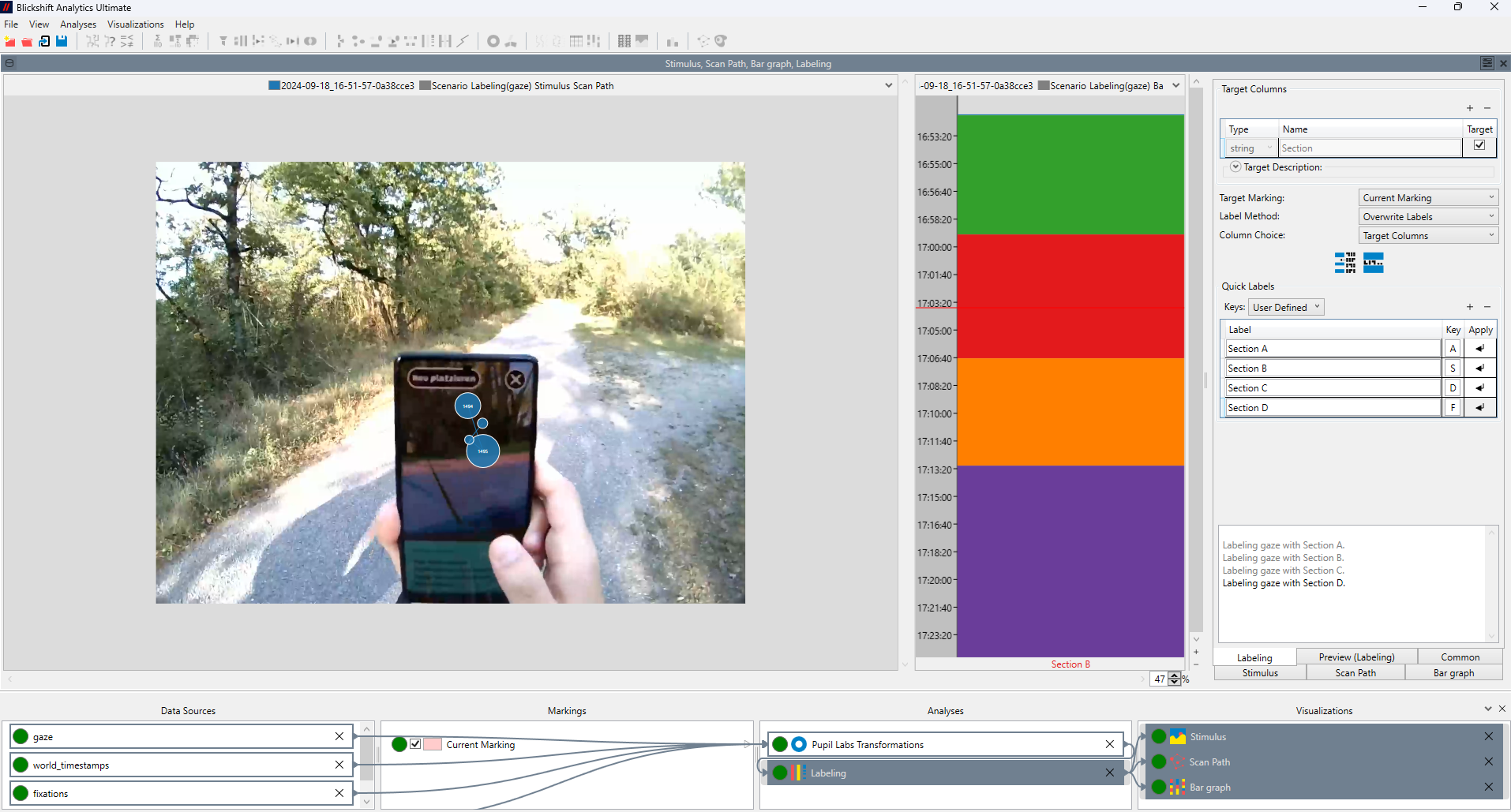
Dynamic Areas of Interest (AOIs) powered by local AI
Challenge: In real-world tasks, objects of interest move and change shape, making AOI analysis difficult.
- Blickshift Analytics enables the definition of dynamic AOIs that can be moved, resized, and adjusted directly in the scene video. One easy-to-use interface gives you full control over any created dynamic AOI at any moment of your recorded videos. You only need to annotate the keyframes of your experiment. The rest of the annotation process is handled by our software by automatically interpolating the AOI trajectories between these keyframes. With this feature, we significantly reduce the time required to analyse eye-tracking data.
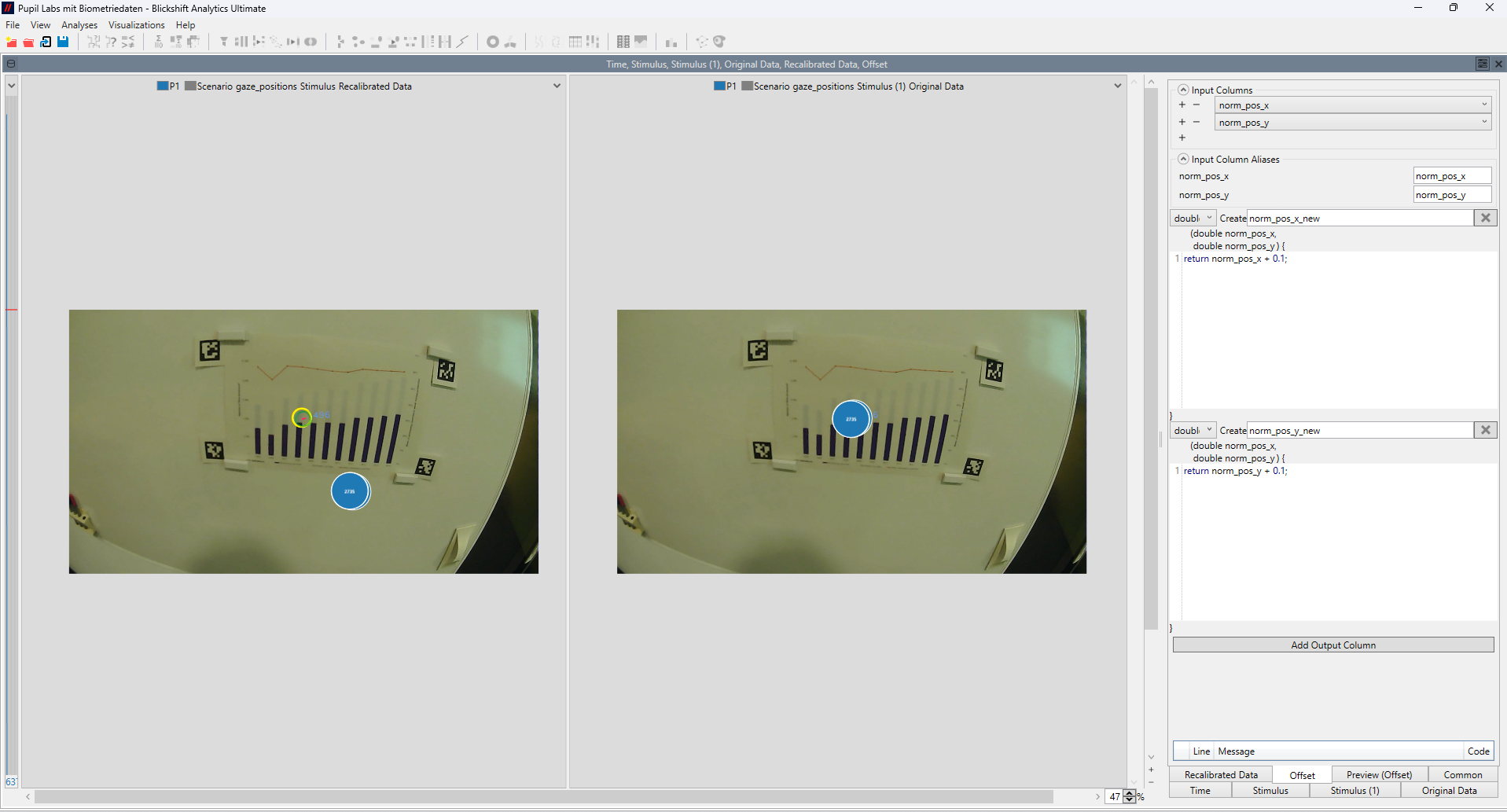
Handling Calibration Drift and Accuracy
Challenge: Calibration errors and drift can occur due to headset movement or lighting changes, reducing data quality over time.
- Blickshift Analytics includes data quality checks and visualization tools that highlight drift or offset in gaze data. Users can identify problematic segments quickly and correct them through filtering or recalibration steps — ensuring consistently accurate gaze mapping throughout the experiment.
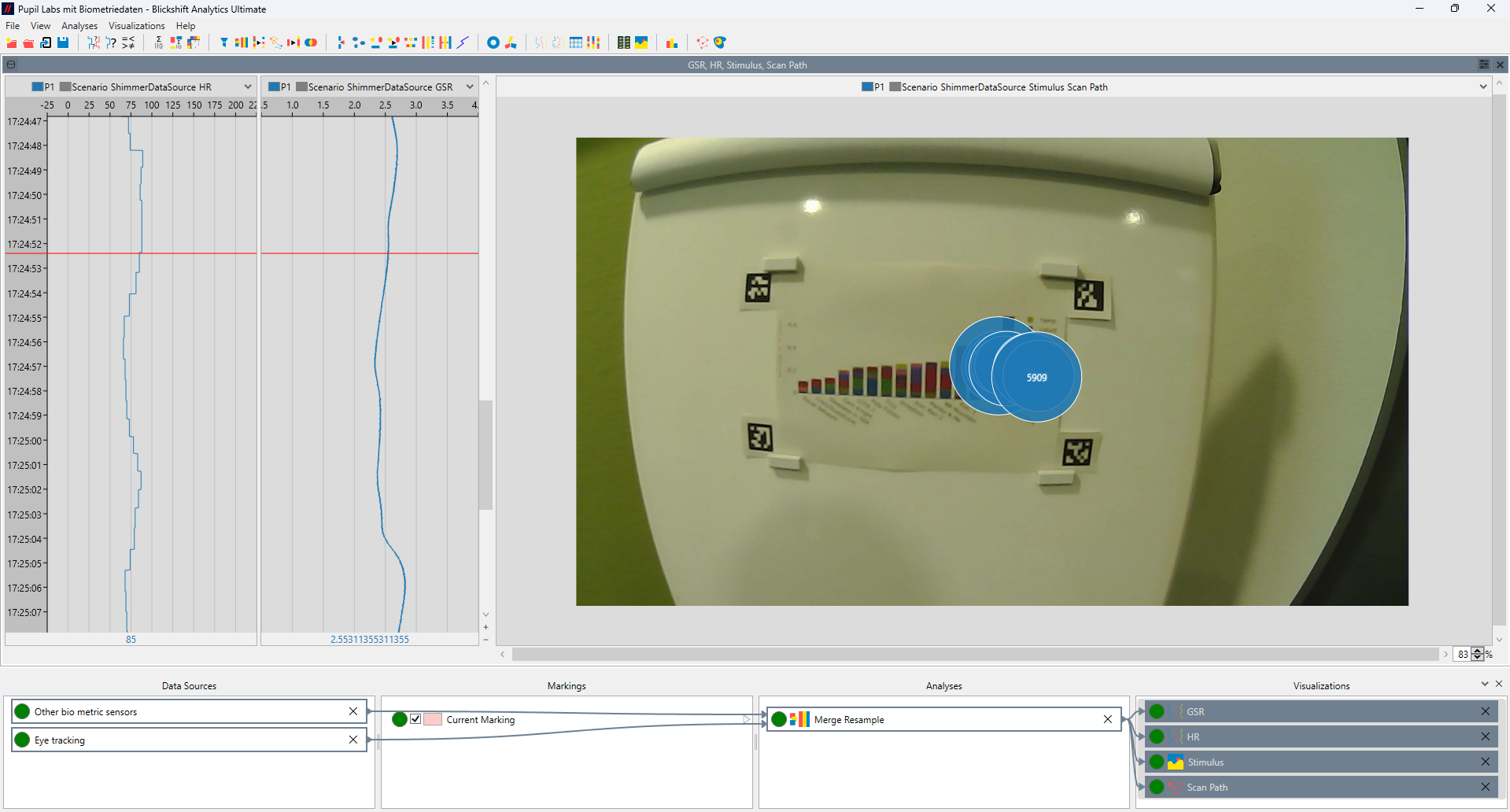
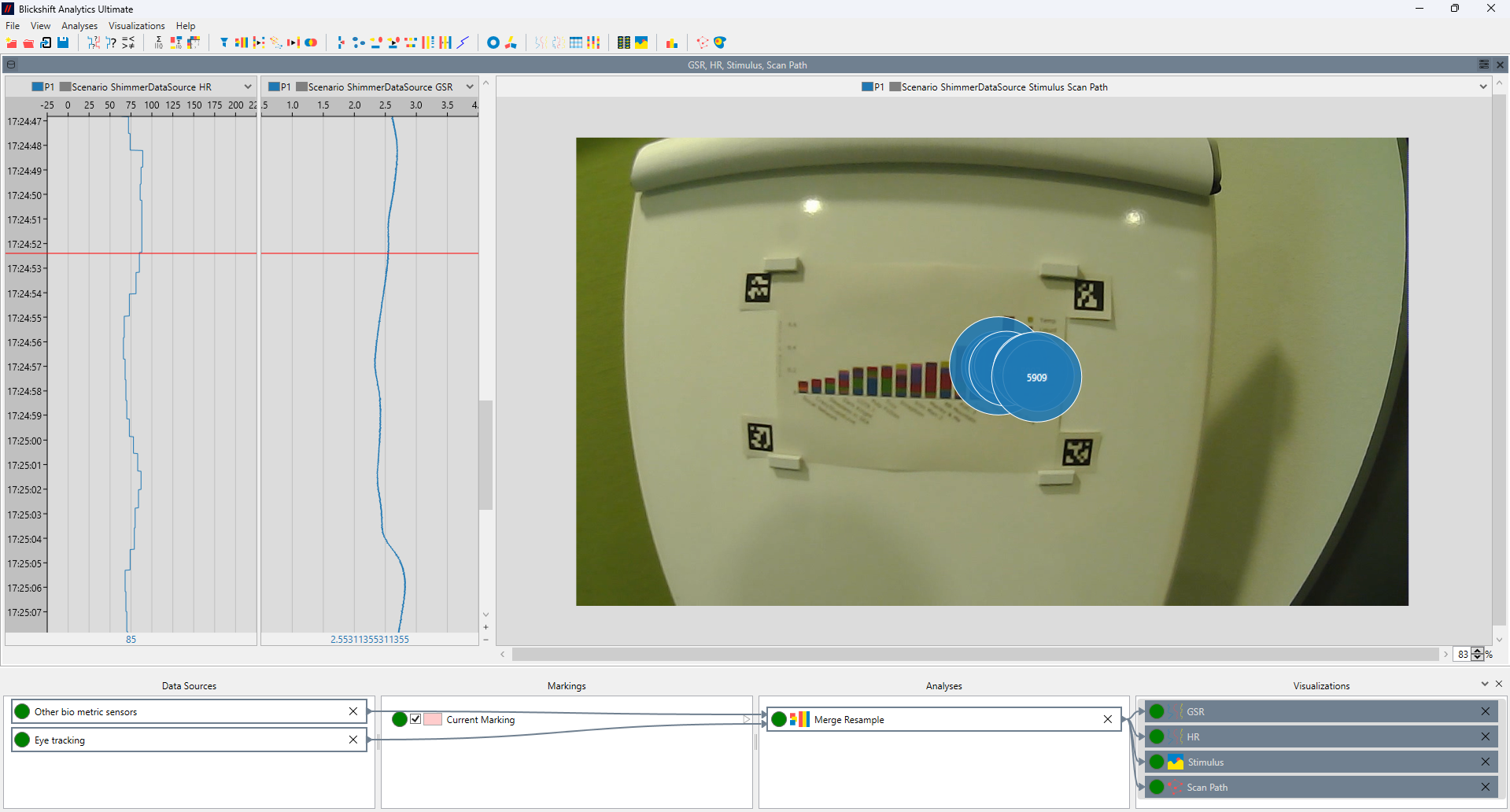
Precise Synchronization of Data Streams
Challenge: Eye, other sensors, and scene data often come from different sources with different timestamps. Misalignment can distort analysis results.
- The software’s flexible timeline view synchronizes multiple data streams (e.g., gaze, scene video, physiological data or motion capture) with millisecond precision. Researchers can easily align events and visualize temporal relationships between signals, ensuring valid and reproducible results.
Event and Context-Based Analysis
Challenge: In naturalistic recordings, identifying relevant events or stimuli is time-consuming and error-prone.
- Blickshift Analytics supports event-based synchronization and segmentation. Researchers can tag and organize events, automatically align them with gaze data, and quickly filter by specific task phases or stimuli. This makes it easy to analyze how gaze behavior changes in response to context.
Differentiating Head and Eye Movements
Challenge: Head-mounted systems often produce noisy or incomplete gaze data.
- Blickshift Analytics includes advanced filtering, interpolation, and smoothing options to improve data quality. Our platform highlights missing or unreliable samples and provides tools to clean and preprocess data before further analysis, ensuring robust, reproducible results.
Reliable Data Quality and Filtering
Challenge: In head-mounted setups, head and eye movements are intertwined, complicating the interpretation of gaze behavior.
- Blickshift Analytics allows visualization of gaze trajectories in combination with head movement data. By linking both data streams, the software helps distinguish between head-driven and eye-driven gaze shifts, enabling a more precise understanding of visual attention dynamics.